In the world of audio production, there are various technical terms and concepts that are important to understand. Two such concepts are audio sample rates and bit depth. These parameters are critical to determining the quality and fidelity of digital audio.
In this blog, we’ll delve into what is sample rates and explore the role of bit depth. What’s more, we’ll look at what sample rate/bit depth should you record at.
What are sample rates?
Sample rates refer to the number of audio samples captured per second during the analog-to-digital conversion process. They are measured in Hertz(Hz). In simpler terms, the sample rates determine how many times the audio signal is “sampled” per second. The reproduction of audio is usually better when the sample rate is higher. The more samples you take, the more closely the final digital file will resemble the original musical source.
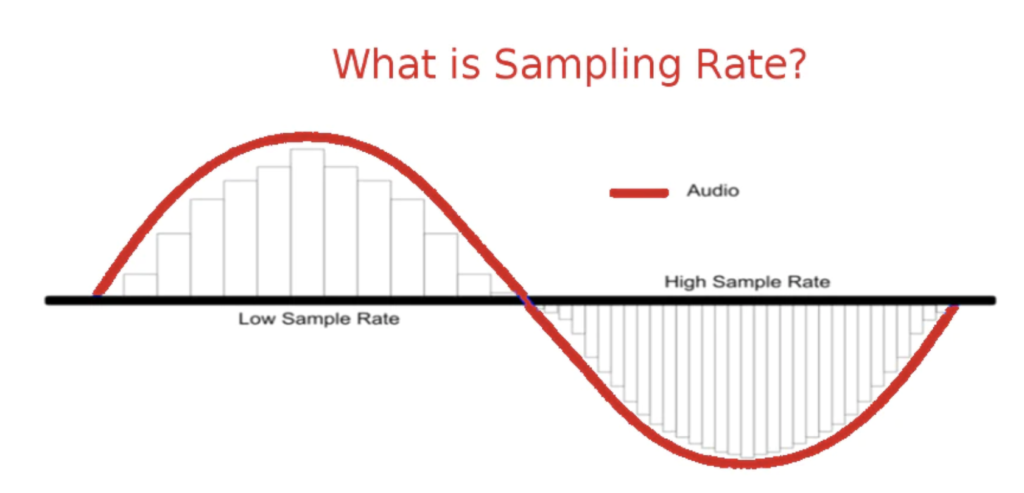
If you can master sample rates, you can create more accurate recordings. The final sound quality of your recording relies on more than just sample rate – bit depth also plays its part.
What is bit depth?
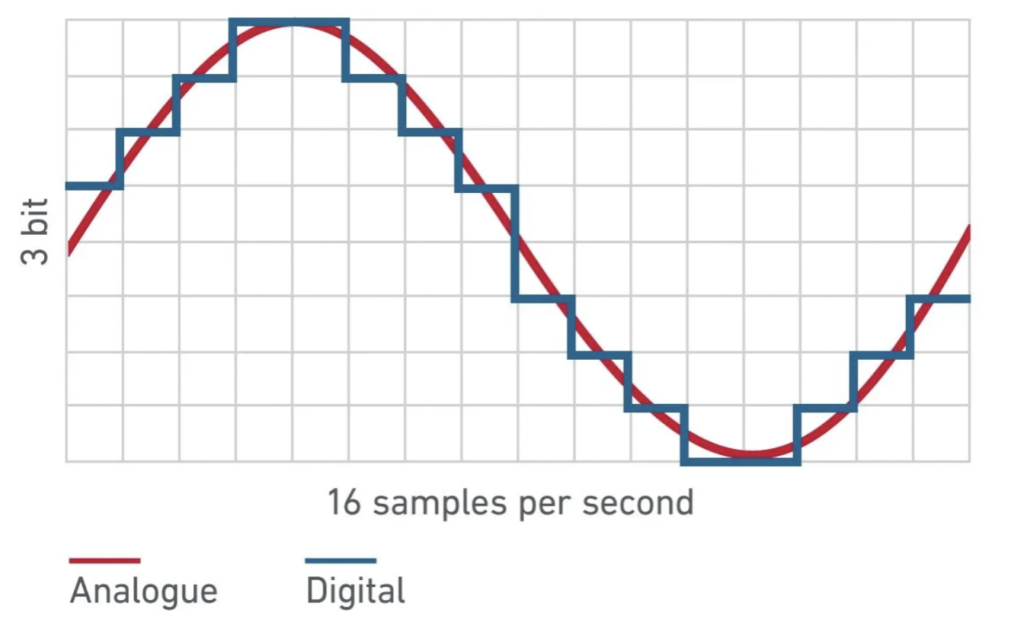
Bit depth refers to the number of possible amplitude values we can record for each audio sample. It indicates the precision and dynamic range of the digital audio signal.
You need to store every sample in your computer’s ‘bits’ when you record audio. You get better sound reproduction when you record each sample with more bits. In other words, you will achieve the best audio quality in your recording with a high sample rate and a high bit depth.
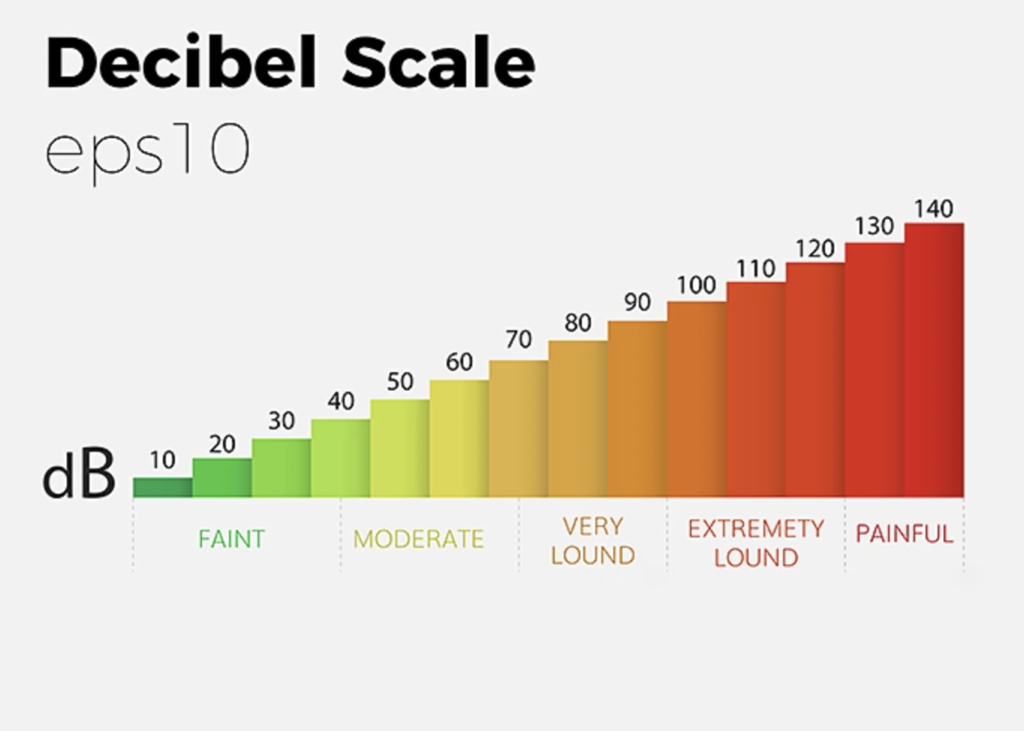
A recording’s dynamic range is the difference between the low volume and high volume sections. Usually, high bit depths result in greater dynamic ranges. A decibel – or dB – is used to measure this.
What should my bit depth be?
In audio, 16-bit, 24-bit, and 32-bit are the most common bit depths. They represent a number of possible values.
8-bit audio: This is a fairly low-quality reproduction, producing audio at 46dB – around half the top level of human hearing.
16-bit audio (65,536 values): This is where the human ear can usually hear at 96dB. So it is usually the standard CD format.
24-bit audio (16,777,216 values): Professional audio production usually uses it widely. It provides a dynamic range of approximately 144 dB, allowing for capturing and reproducing subtle audio nuances with greater accuracy.
32-bit audio (4,294,967,296 values): The choice of bit depth depends on your specific audio recording and production requirements.
How to determine an appropriate bit depth?
Dynamic Range: Consider the dynamic range of your audio source. If you’re working with a wide range of volume levels, such as in orchestral recordings or sound design, a higher bit depth like 24-bit or 32-bit can capture more detail and maintain fidelity in soft or quiet passages.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio: Higher bit depths offer a greater signal-to-noise ratio, reducing the audible noise floor and providing cleaner recordings. If you require precise, noise-free audio, especially in quieter recordings or when applying extensive post-processing, higher bit depths are beneficial.
Workflow and Compatibility: Assess your workflow and the compatibility of your equipment and software. While higher bit depths offer advantages in audio quality, they require more processing power and storage space. Ensure that your recording setup, audio interface, and software support your desired bit depth.
Distribution Format: Consider the final distribution format of your audio. If you’re producing content for CD, streaming platforms, or broadcast, a 16-bit depth may be sufficient since these formats often use 16-bit audio. However, if your content targets high-resolution audio formats or specialized platforms, higher bit depths may be necessary.
In general, for most musical applications and typical listening scenarios, a 16-bit or 24-bit depth is often suitable and provides excellent results. However, if you require maximum audio quality, capturing a wide dynamic range, or working in professional audio production, opting for a higher bit depth such as 24-bit or 32-bit is recommended.
What sample rate should I record?
The common sample rates are 44.1 kHz, 48 kHz, 96, kHz, and 192 kHz. This allows for greater resolution in all mixing and effects and gives you the flexibility of bouncing down to a sample rate compatible with your medium of distribution. When bouncing down your audio, however, you’ll need to pick a bit depth and sample rate that are compatible with your medium.
44.1 kHz vs. 48 kHz
When recording music, the widely adopted sample rate is 44.1 kHz (44,100 samples per second). It is standard in consumer audio and formats like CDs. Another frequently employed sample rate is 48 kHz, commonly found in movie audio. The higher sample rate provides a greater number of measurements per second, resulting in a more faithful reproduction of the original audio. As a result, 48 kHz is often utilized in video audio production, where a significant dynamic range is required.
96 kHz vs. 192 kHz
Recording at a sample rate of 192 kHz, which captures twice as many samples per second compared to 96 kHz, will need to double the hard-drive space for storage. Using higher sample rates like 96 kHz and 192 kHz can allow for maximum audio resolution. However, it places significant demands on processing power, and the discernible difference to the human ear is often minimal. In most musical scenarios, recording at 48 kHz using a quality audio interface will produce outstanding outcomes.
Why use 44.1 kHz as CD standard format?
The human auditory system has a limited frequency range of approximately 20Hz to 20kH. To accurately reproduce audio, It is necessary to sample at twice the maximum audible frequency according to the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem. Hence, we choose 44.1kHz as it provides a comfortable margin above the upper limit of human hearing.
Furthermore, the 44.1kHz sample rate simplifies compatibility across different audio devices and systems. It has become an industry standard, and audio equipment, software, and digital platforms widely support 44.1kHz. Like our top-selling device – YoloBox Pro, also support audio input format such as 32kHz/44.1kHz/48kHz/16-bit/16kHz.

Conclusion
Understanding audio sample rates and bit depth is essential for audio production. Sample rate determines the frequency at which audio is captured, while bit depth affects the precision and dynamic range of the digital audio signal. While higher sample rates and bit depths offer potential advantages, the optimal settings depend on the specific requirements of the project. By considering factors such as target platforms, storage space, and processing power, you can make informed decisions when it comes to choosing sample rates and bit depths.
For more Pro AV industry general knowledge, please check out YoloLiv’s blog.
37,700 total views, 3 views today

Meredith, the Marketing Manager at YoloLiv. After getting her bachelor’s degree, she explores her whole passion for YoloBox and Pro. Also, she contributed blog posts on how to enhance live streaming experiences, how to get started with live streaming, and many more.